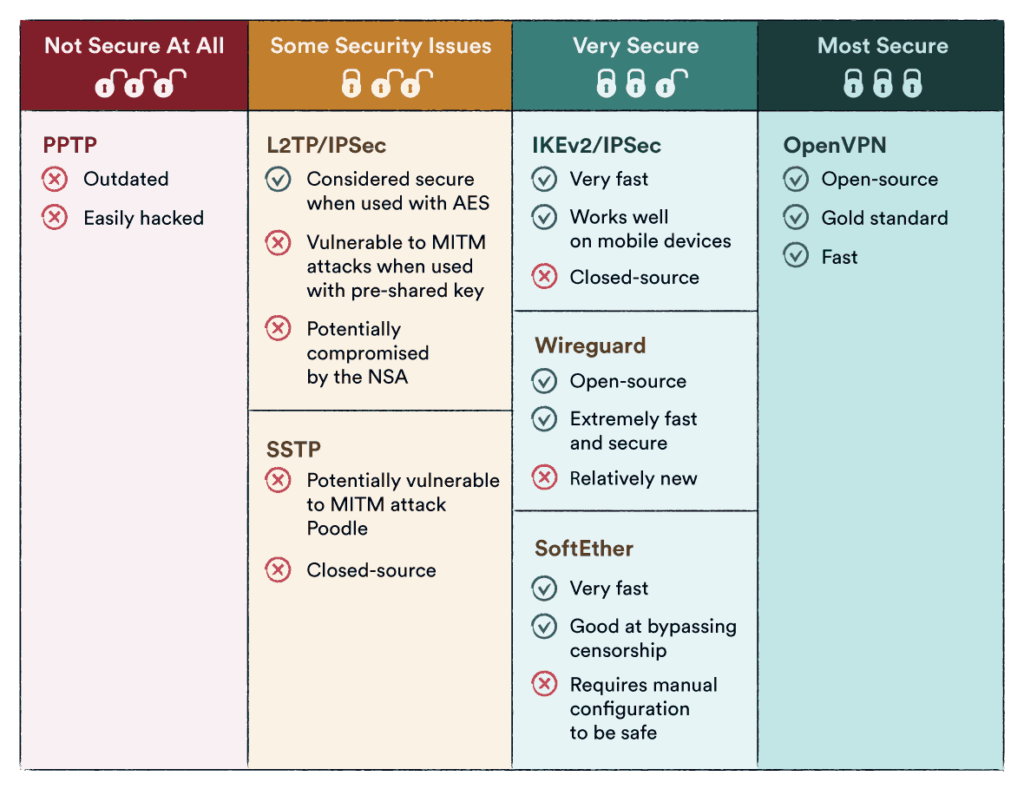
Types of tunneling VPN protocols and choosing the best one
- PPTP control connection creates, maintains and terminates the tunnel. This is done using various management messages. PPTP Echo-Request and PPTP Echo- Reply-detect, connectivity failure between serve and client. PPTP control packet consists of IP header, TCP header, PPTP control message and a data link trailer. For more information about the exact structure of PPTP control messages search for RFC 2637 in the RFC database.
- GRE-Generic Routing Encapsulation is used to encapsulate PPP frames as tunneled data. The initial PPP payload is encrypted and encapsulated with PPP. This PPP frame is then encapsulated with a modified GRE header. GRE is described by RFC 1701 and RFC 1702. The Packet now has a Data link header, IP header, GRE Header, PPP Header, Encrypted PPP payload and Data link trailer.
- PPTP payloads that have been encapsulated can be either encrypted or compressed. Sometimes both encryption and compression are done.
- Authentication mechanisms in PPP connections are used by PPTP. EAP-Extensible Authentication protocol, MS-CHAP- Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol, SPAP-Shiva Password Authentication protocol and PAP- Password Authentication Protocol are the other authentication protocols that can be used.
- For encryption that uses MPPE-Microsoft Point to Point Encryption of PPP, EAP-TLS, MS-CHAP or MS-CHAPv2 authentication must be used. PPTP inherits encryption as well as compression from PPP. These can be implemented independently or both together. This only is a link and end-to-end encryption is not provided by PPTP.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol
IETF describes L2TP in RFC 2661. L2TP represent the best features of PPTP and L2F-Layer 2 Forwarding protocols. It encapsulates PPP frames to be sent over IP, X.25, Frame relay or ATM networks. If IP network is used L2TP frames are encapsulated as UDP-User Datagram Protocol. L2TP can be used over the internet as well as over private intranets.
- L2TP control messages are sent over the IP network between an L2TP client and L2TP server as UDP messages. Even data uses UDP messages. For Windows UDP port 1701 is used. For Windows server 2003 UDP datagrams are sent as an encrypted payload of IPSec. The packet consists of data link header, IP Header, IPSec ESP Header, UDP header, L2TP message, IPSec ESDP trailer, IPsec ESP Auth trailer and Data Link trailer.
- Payloads of PPP can either be encrypted or compressed. Both Encryption and compression can be done.
- ESP- Encapsulating Security Payload of IPSec provides the encryption for L2TP in Transport mode. IPSec is used for both authentication and encryption. Non-encrypted L2TP connections can be established by windows based software. Authentication here involves PPP authentication mechanisms.
- An Internet-based L2TP server is an L2TP-enabled remote access server with one interface on the Internet and a second interface on a private intranet.
- L2TP tunnel maintenance and tunneled data have the same packet structure and it supports multiple calls for each tunnel. L2TP control message and header for data is the tunnel ID that identifies the tunnel.
- L2TP encapsulation involves the encapsulation of a PPP payload with a PPP header and a L2TP header. UDP encapsulation is done on the L2TP packet which provides a UDP header and source and destination ports are set to 1701. The UDP message is encrypted and encapsulated with an IPSec ‘ESP header and trailer’ and ESP authentication trailer.
- IPSec provides two protocols Authentication Header AH and ESP.
IPSec (IP Security)
IPsec (IP security) is an evolving internet standard for securing Internet Protocol (IP) communications by encrypting and/or authenticating all IP packets. IPSec provides security at the network layer. It is a part of IPv6 (Internet protocol version6) and can be used with IPv4. RFCs 2401-2412 define IPsec protocols. IKE- Intenet Key Exchange protocol is the most recent update of IPSec.
- IPSec creates and maintains its own tunnel in tunnel mode where portal to portal communications security is provided.
- IPSec’s transport mode only provides authentication and encryption for end to end communications.
VPN’s can be created in either mode. Implementations in either mode have different security implications. IPSec protocols are to secure packet flows and key exchange (IKE).
- Encapsulation Security Payload provides authentication, Data confidentiality and message integrity.
- Authentication Header provides for authentication and message integrity but does not offer confidentiality.
- Sending and receiving devices must share a public key; the implementation of which is done by a protocol known as Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol/Oakley (ISAKMP/Oakley). This allows the receiver to obtain a public key and authenticate the sender using digital certificates.
IPSec tunnels can be any of several types.
- IPSec/PPTP tunnels use PPTP tunnel protocol with IPSec encryption.
- IPSec/L2TP tunnels use L2TP (Level-2 Tunnel Protocol) to establish the tunnel and then run IPSec encryption on it.
- IPSec/GRE tunnels layer IPSec directly onto plain GRE tunnels
SSL VPN protocol
SSL- Secure Sockets Layer and TLS- Transport Layer Security a successor to SSL are cryptographic protocols for secure communications over the internet. SSL tunneling usually applies to both the protocols
- SSL provides endpoint authentication and privacy for communications.
- In typical use only server is authentication while the client is not. Mutual authentication requires PKI- Public Key infrastructure deployment to the Client.
- Public Key Encryption (RSA, Diffie-Hellman, DSA or Fortezza;) and certificate based authentication is followed by SSL
- Traffic encryption is based on a symmetric cipher (RC2, RC4, IDEA, DES, Triple DES or AES).
- Split tunneling for end users to have access to internet and intranet simultaneously. VPN split tunneling security is important in VPN servers.
Choose your VPN Protocol
The best choice of protocols for your organization depends on a number of factors: server and client operating systems deployed, network resources to which access is needed, level of security required, performance issues, administrative overhead and so forth.
PPTP
PPTP is the most widely supported VPN method among Windows clients.
- It is link layer protocol which has a low overhead making it faster than other VPN methods.
- EAP authentication uses digital certificates for mutual authentication and eliminates the earlier security flaws of PPTP.
- Public Key Infrastructure is not required
Many firewall based enterprise level software support PPTP. (ISA server, CISCO PIX, SonicWALL). The other operating systems that incorporate them or can incorporate them are
- For windows based clients, the software’s already incorporate PPTP.
- For Linux PPTP client see http://pptpclient.sourceforge.net/
- Mac OS X 10.2 see http://www.rochester.edu/its/vpn/tunnelbuilderl
- OS X see http://www.gracion.com/vpn/
L2TP
L2TP’s main advantage is that it can be used over non-IP networks such as ATM, Frame relay, and X.25. It operates at the data link layer.
- L2TP uses digital certificates and also provides computer authentication. This adds an extra level of security. User authentication can be performed via the same PPP authentication mechanisms as PPTP.
- L2TP gives you data confidentiality which is not present in PPTP. Data integrity, ‘authentication of origin’ and replay protection are added advantages.
- Extra Security measures slightly slow the performance when compared to PPTP.
- IPSec’s Encapsulating Security Payload protocol, provides the encryption for L2TP tunnels.
Many Firewall products support L2TP VPNs. (including ISA Server, CheckPoint, Cisco PIX, and WatchGuard)
- Windows 2000, XP and 2003 is incorporated with L2TP protocol. It can be downloaded for the other versions of Windows.
- Software that supports L2TP for Linux and MAC OS can be down loaded from the internet.
IPSec
IPsec is known for its use with L2TP for encryption. It can be considered as a VPN solution for a VPN gateway-to-gateway. IPSec operates at the network layer.
- IPSec works only in IP based networks
- It requires that the client computer have the required software
- Authentication is done by IKE- Internet Key Exchange protocol with either digital certificates or with pre shared keys.
- IPSec protects against most common attack methods including Denial of Service and “man-in-the-middle” attacks.
Many hardware VPN appliances use an implementation of IPSec (Cisco’s VPN Concentrators and PIX firewalls, NetScreen, SonicWall, and WatchGuard appliances)
- Windows 2000/XP/2003 support IPSec. ISA server also supports IPSec.
- CheckPoint and Symantec Enterprise Firewall also support IPSec VPNs.
SSL
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN is growing in popularity because it does not need special VPN client software on the VPN clients. SSL VPN uses the Web browser as the client application and so is called as “clientless” solution.
- Clients do not have access to the whole network or subnet as with other protocols.
- Custom programming is necessary in Java or Active-X to enable other applications to access VPN through the Web Browser.
- The disadvantage is client browser settings need to be opened up to active content which exposes the browser to malicious content. Unsigned active content can be blocked and plug-ins is digitally signed.
Virtual private networking is a cost effective way to provide remote access to your company network. Selection of the proper tunneling method decides your level of security.

ExpressVPN Fast, anonymous browsing all over the world | ||
NordVPN Enjoy online privacy and security with a reliable VPN | ||
Cyber Ghost Browse anonymously with reliable security | ||
SurfShark Affordable and reliable VPN for secure browsing | ||
ZenMate Experience the internet anonymously | ||
Purevpn Keep your data secure with a VPN built for privacy |